In accordance with Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) regulations, employers must carry out regular audits of the OSH Management System. The purpose of such audits is to verify the effective application of the system with respect to occupational risks as well as to the safety and health of employees.
OSH audits are standardized, independent, and documented processes conducted to assess the efficacy of an OSH Management System and to determine the level of compliance with the requirements and criteria established by said system. Thus, these audits allow employers to identify any non-compliance with specific aspects of OSH regulations that may have not been noticed by Management.
OSH regulations provide for 2 audit scenarios: internal and external audits. For further details, please refer to the descriptive table below:
| |
Internal Audits |
External Audits |
| Purpose |
|
Verify if the OSH Management System has been implemented, and if it is appropriate to prevent occupational risks and to ensure the safety and health of employees. |
| Frequency |
-
Annually, applicable to all employers.
-
Once the execution of the Annual OSH program has been completed, and before starting the updating of the OSH Management System documents and tools.
|
-
Every 2 years in the case of employers who perform high-risk activities.
-
When requested by the National Superintendency of Labor Inspections (SUNAFIL) in the case of employers who do not perform high-risk activities and have up to 10 employees.
-
Every 3 years in the case of employers who do not perform high-risk activities and have more than 10 employees.
|
| Responsible Party |
|
Independent auditor currently registered in the Registry of Auditors Authorized by the Ministry of Labor and Employment Promotion (MINTRA). . |
Process to elect an Independent Auditor
Companies must elect an independent auditor who is currently registered in the Registry of Auditors Authorized by the MINTRA, considering the specialty, size, type of activities performed, and level of risk of the employer.
Said independent auditor will be elected with the participation of all employees and the General Management, and the election process must be carried out as follows:
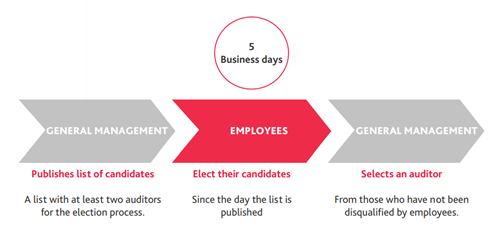
Mandatory nature of the Audits
Even though SST regulations set out that audits must be mandatorily carried out since 2011, external audits were suspended during the State of Health Emergency declared as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. Said regulations later established that employers had 90 calendar days after the end of the State of Health Emergency to conduct such audits. Given that the health emergency ended in May 2023, external audits must be mandatorily conducted since August 2023 in the case of employers who perform high-risk activities and in the case of those employers who do not perform high-risk activities but have more than 10 employees.
The failure to conduct such audits may give rise to penalties that may range from 0.26 tax units (S/ 1,287.00) and 52.53 tax units (S/ 260,023.50), based on the nature of the infraction committed and the number of affected employees.
At BDO, we have a specialized and multidisciplinary team that can provide the necessary advisory to ensure optimal compliance with Occupational Safey and Health obligations, in connection with the audits and the implementation of the OSH Management System, among others.